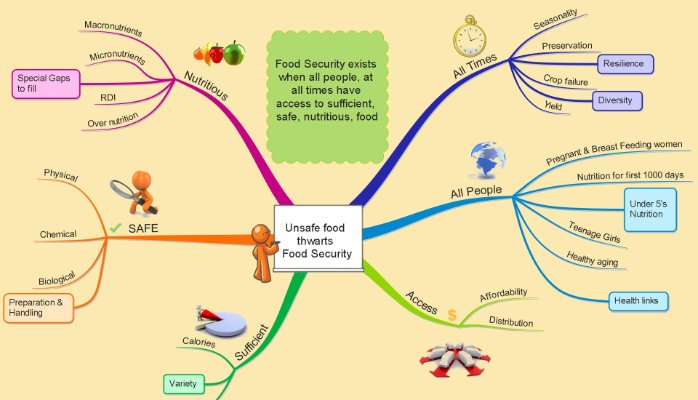
A majority of reported food borne illness outbreaks, 8 in every 10, originate from food prepared in commercial settings. The most common cause of acute gastroenteritis in the United States, Norovirus, is perpetuated by sick food handlers in 53% of all cases. Other sources of foodborne illness include bacteria such as Salmonella and E. coli, viruses, parasites, and chemicals.
The most common symptoms of food poisoning include vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, fever, or chills. More serious cases can affect the central nervous system, and include symptoms such as headache, tingling or numbness of the skin, blurred vision, weakness, dizzyness, or paralysis.